How can we help?
Search for answers or browse our knowledge base
calculation engine
Overview
- A sheet is limited to 4095 columns and 1048575 rows.
- Function names and booleans are in the user’s locale. Supported locales are :
English, Danish, Dutch, Finnish, French, German, Italian, Norwegian, Portuguese, Spanish, Swedish. In other cases, the calculation engine switches to English.
- The engine uses the user’s locale, including the argument separator.
- References are in A1, supporting relative and absolute references, row or column, but not 3D references (e.g., =SUM(Sheet1:Sheet3!A1)), which will be advantageously replaced by a multi-tab which offers elaborate synthesis functions.
Errors
The errors reported are the following:
| Error | Remarks | Excel compatible |
| #CIRCLE! | The cell is part of a cycle | |
| #DIV/0! | YES | |
| #N/A | YES | |
| #NAME? | Function, unknown name | YES |
| #NUM! | YES | |
| #PARAM! | Wrong number of parameters when calling a function | |
| #SYNTAX! | The syntax of the formula is not correct for the Calame engine | |
| #REF! | Invalid reference YES | |
| #VALUE! | YES | |
| #NOTSUPPORTED | Specific formula function or expression not supported in GT | |
| #UNKNOWN! | Unknown error, reports a bug in the engine |
Date management
The calculation engine does not support the “Calendar since 1904” Excel option
Dates strictly inferior to 01/03/1900 are not compatible with Excel.
Particularly the functions taking a date as input (MONTH, DAY,…) do not work in the same way as Excel with empty values.
Thus, MONTH(Ø) = 12 in GT and 1 in Excel (because the serial number date 0 is 12/12/1899 in GT and 00/01/1900 in Excel).
Functions
Overview
- The volatile functions are recalculated as in Excel, i.e., at each evaluation. The volatile functions are :
ALEA, ALEA.ENTRE.BORNES, TODAY, NOW, INDIRECT, SHIFT
- Matrix formulas are not supported
- Function names are not case-sensitive.
- Functions returning text have no limit of 32767 characters except REPT.
- Some Excel functions work differently depending on whether a parameter is a value or a reference. For example,
AND(TRUE; “AAAAA”) returns #VALUE! while AND(TRUE;A1) with A1=”AAAAA” returns TRUE. The grid engine does not differentiate between these two cases. In the example above, it always returns TRUE.
- Excel functions that deal with integers return an inconsistent result if the integer exceeds 2^53 (double precision). For example for GCD(2^60 ;2^60-1) = GCD(1152921504606846976, 1152921504606846975) Excel returns 1,…E18 when the result is 1. Some GT functions will check that the operands do not exceed the limit and return #NUM! if they do (e.g. GCD and LCM). These cases are indicated in the function list.
Functions with string criteria (for NB.IF, SUM.IF, SUM.IF.ENS…)
If the criterion contains ‘*’, ‘?’, the character will be interpreted as a wildcard (in the same way as Excel).
The protection character of these wildcards is ~
In addition, string criteria are limited to 255 characters in Excel. The GT engine does not have this limitation.
List of the engine functions
GT specific functions
| Name (EN) | Name (FR) | Syntax | Remarks |
| GTDISPLAYTEXT | GTDISPLAYTEXT | GTDISPLAYTEXT (cell) | Returns the text displayed by the cell (takes into account the numeric format) |
| GTHASH (deprecated as of version 2019) | GTHASH | GTHASH(range, [algo, DoPj, SkipEmpty]) | Algo = CRC32 or MD5 (default)
DoPj : boolean SkipEmpty: boolean |
| GTMOAXIS | GTMOAXIS | GTMOAXIS([offset]) | Returns the name of the multi-tab group axis in a multi-tab group |
| GTMOAXISVAL | GTMOAXISVAL | GTMOAXISVAL([offset]) | Returns the current (or previous/following) item in a multi-tab |
| GTMOGETSHEETNAME | GTMOGETSHEETNAME | GTMOGETSHEETNAME(item [, Axis, tab_index] ) | returns the name of the grid/sheet for the item in a multi-tab, Axis and tab_index allow to specify the multi-tab group and/or the tab number in a multi-tab group with several sheets to be expanded |
| GTMS | GTMS | GTMS.Function_GTMS(argument) | Used to aggregate the data of a multi-tab. See the detailed article Data synthesis of a multi-tab |
| GTPATNUM | GTPATNUM | GTPATNUM([reference]) | Returns the “row” number in a pattern. See detailed article GTPATNUM |
| GTSGMO | GTSGMO | GTSGMO(‘Grid’!ref) | Summarizes the values of a cell on the sheets of a multi-tab group. The name of the grid is mandatory. |
| GTVALIDMAILADDRESS | GTVALIDMAILADDRESS | GTVALIDMAILADDRESS() | Returns the email address, if validated, in Answer (validation process via .checkmail attachment) |
| GTADMAILADDRESS | GTADMAILADDRESS | GTADMAILADDRESS() | Returns the email address of the AD account used for authentication in Answer (authentication is enabled via the campaign launch action) |
| GTPJSIZE | GTPJSIZE | GTPJSIZE(ref_cell) | Returns the size of the file saved in the attachment component located in “ref_cell |
Date & Time
| Name (EN) | Name (FR) | Syntax | Remarks |
| DATE | DATE | DATE(year, month, day) | |
| DATEVALUE | DATEVAL | DATEVALUE(date_text) | Only supports date_text in dd/mm/yy[yy] (local) formats |
| DAY | JOUR | DAY(serial_number) | |
| DAY360 | JOUR360 | ||
| EDATE | MONTH.DECALER | EDATE(start_date,months) | Range => #VALUE! |
| EOMONTH | FIN.MOIS | EOMONTH(date, month) | |
| HOUR | HEURE | HOUR(serial_number) | |
| ISOWEEKNUM | HOUR.ISO | ISOWEEKNUM(date) | Excel >= 2013, GT >= 3.9 |
| MONTH | MOIS | MONTH(serial_number) | |
| NETWORKDAYS | NETWORKDAYS(start_date, end_date, [holidays]) | ||
| NETWORKDAYS.INTL | NB.JOURS.OUVRES.INTL | NETWORKDAYS.INTL(start_date, end_date, [weekend], [holidays]) | |
| NOW | MAINTENANT | NOW( ) | |
| SECOND | SECONDE | SECOND(serial_number) | |
| TIME | TEMPS | TIME(hour, minute, second) | |
| TIMEVALUE | TEMPSVAL | TIMEVALUE(time_text) | |
| TODAY | AUJOURDHUI | TODAY() | |
| WEEKDAY | JOURSEM | WEEKDAY(serial_number,return_type) | |
| WEEKNUM | NO.SEMAINE | WEEKNUM(serial_num,return_type) | Range => #VALUE!return_type >= 21 from GTv3.9 |
| ISOWEEKNUM | NO.SEMAINE.ISO | ISOWEEKNUM(serial_num) | from GTv3.9 equivalent to WEEKNUM with return_type to 21 |
| YEAR | ANNEE | YEAR(serial_number) |
Information
| Name (EN) | Name (FR) | Syntax | Remarks |
| ERROR.TYPE | TYPE.ERREUR | ERROR.TYPE(val_error) | GT errors the values are >= 100:
#SYNTAX ! : 100 ERROR.TYPE For #CIRCLE! : 101 #PARAM! : 102 #UNKNOWN! : 103 |
| ISBLANK | ESTVIDE | ISBLANK(value) | |
| ISERR | ESTERR | ISERR(value) | |
| ISERROR | ESTERREUR | ISERROR(value) | |
| ISEVEN | EST.PAIR | ISEVEN(number) | Range => #VALUE! |
| ISLOGICAL | ESTLOGIQUE | ISLOGICAL(value) | |
| ISNA | ESTNA | ISNA(value) | |
| ISNONTEXT | ESTNONTEXTE | ISNONTEXT(value) | |
| ISNUMBER | ESTNUM | ISNUMBER(value) | |
| ISODD | EST.IMPAIR | ISODD(number) | Range => #VALUE! |
| ISTEXT | ESTTEXTE | ISTEXT(value) | |
| N | N | N(value) | Range => TopLeft |
| NA | NA | NA() | |
| TYPE | TYPE | TYPE(value) |
Logic
| Name (EN) | Name (FR) | Syntax | Remarks |
| AND | ET | AND(logical1, [logical2], …) | |
| FALSE | Faux | FALSE() | |
| IF | SI | IF(logical_test, [value_if_true], IF [value_if_false]) | |
| IFERROR | SIERREUR | IFERROR(value,value_if_error) | Excel 2007 and > function |
| NOT | NON | NOT(logical) | |
| OR | OU | OR(logical1,logical2,…) | |
| TRUE | Vrai | TRUE() |
Search & Reference
| Name (EN) | Name (FR) | Syntax | Remarks |
| ADDRESS | ADDRESSE | ADDRESS(row,column,[abs_num],[a1],[sheet_name_txt]) | Parameter A1 is ignored, the result is always produced in style A1 |
| CHOOSE | CHOISIR | CHOOSE(index_num,value1,value2,…) | |
| COLUMN | COLONNE | COLUMN(reference) | |
| COLUMNS | COLONNES | COLUMNS(range) | |
| HLOOKUP | RECHERCHEH | HLOOKUP(lookup_value,table_array, row_index_num,[range_lookup]) | |
| INDEX | INDEX | INDEX(array,row_num[,column_num]) | Excel compatibility
* no syntax handling with field numbers * By default, column_num is 1 as in Excel * Returns #VALUE! if column_num = 0 |
| INDIRECT | INDIRECT | INDIRECT(range_or_text[,a1]) | Always in A1, the second parameter is ignored |
| ISREF | ESTREF | ESTREF(value) | |
| LOOKUP | RECHERCHE | LOOKUP(lookup_value,lookup_vector,result_vector)
or LOOKUP(lookup_value,array) |
Excel compatibility:
* GT returns #N/A if lookup_vector or result_vector is not a vector (Excel only for result_vector) * GT returns #N/A if lookup_vector and result_vector are not the same size |
| MATCH | EQUIV | MATCH(lookup_value,lookup_array,[match_type]) | |
| OFFSET | DECALER | OFFSET(range,rows,columns,[width_rows,[height_columns]]) | Returns #VALUE! when the first parameter is not a reference (Excel forbids the entry of such a formula) |
| ROW | LIGNE | ROW(reference) | |
| ROWS | LIGNES | ROWS(range) | |
| VLOOKUP | RECHERCHEV | VLOOKUP(lookup_value, table_array, col_index_num, [range_lookup]) |
Maths
| Name (EN) | Name (FR) | Syntax | Remarks |
| ABS | ABS | ABS(number) | |
| ACOS | ACOS | ACOS(number) | |
| ACOSH | ACOSH | ACOSH(number) | |
| ASINH | ASINH | ASINH(number) | |
| ATAN | ATAN | ATAN(number) | |
| ATAN2 | ATAN2 | ATAN2(x_num,y_num) | |
| ATANH | ATANH | ATANH(number) | |
| CEILING | PLAFOND | CEILING(number,significance) | |
| COMBIN | COMBIN | COMBIN(number,number_chosen) | |
| COS | COS | COS(number) | |
| COSH | COSH | COSH(number) | |
| DEGREES | DEGRES | DEGREES(angle) | |
| EVEN | PAIR | EVEN(number) | |
| EXP | EXP | EXP(number) | |
| FACT | FACT | FACT(number) | |
| FACTDOUBLE | FACTDOUBLE | FACTDOUBLE(number) | |
| FLOOR | PLANCHER | FLOOR(number,significance) | |
| GCD | PGCD | GCD(number1,number2, …) | Returns #NUM! if any parameter exceeds 2^53 |
| INT | ENT | INT(number) | |
| LN | LN | LN(number) | |
| LCM | PPCM | LCM(number1,number2, …) | Returns #NUM! if any of the parameters or the result exceeds 2^53 |
| LOG | LOG | LOG(number,base) | |
| LOG10 | LOG10 | LOG10(number) | |
| MOD | MOD | MOD(number,divisor) | |
| MROUND | ARRONDI.AU.MULTIPLE | MROUND (number, multiple) | |
| MULTINOMIAL | MULTINOMIALE | MULTINOMIAL(number1,number2, …) | Returns #VALUE! if an argument is of string type (even if the string contains a number. In this case, Excel returns the wrong value because it uses the SUM function internally which does not do this conversion). |
| ODD | IMPAIR | ODD(number) | |
| PI | PI | PI() | |
| POWER | PUISSANCE | POWER(number,power) | |
| PRODUCT | PRODUIT | PRODUCT(number1, [number2], …) | |
| QUOTIENT | QUOTIENT | QUOTIENT(numerator,denominator) | in Excel <= 2003, can return -0 (for example: QUOTIENT(-1,4)) |
| RADIANS | RADIANS | RADIANS(angle) | |
| RAND | ALEA | RAND() | |
| RANDBETWEEN | ALEA.ENTRE.BORNES | RANDBETWEEN(min, max) | |
| RANK | RANG | RANG(number,ref,order) | |
| ROUND | ARRONDI | ROUND(number, num_digits) | |
| ROUNDDOWN | ARRONDI.INF | ROUNDDOWN(number, num_digits) | |
| ROUNDUP | ARRONDI.SUP | ROUNDUP(number, num_digits) | |
| SIGN | SIGNE | SIGN(number) | |
| SIN | SIN | SIN(number) | |
| SINH | SINH | SINH(number) | |
| SQRT | RACINE | SQRT(number) | |
| SQRTPI | RACINE.PI | SQRTPI(number) | |
| SUBTOTAL | SOUS.TOTAL | SUBTOTAL(function_num, ref1, ref2, …) | if function_num is ³ 101 and £ 111 then generate a parameter error |
| SUM | SOMME | SUM(number1, [number2], [number3], [number4], …) | |
| SUMIF | SOMME.SI | SUMIF(range, criteria, [sum_range]) | range must have a number of elements <= to sum_range otherwise => #N/A! (if not, Excel completes range) |
| SUMIFS | SOMME.SI.ENS | SUMIFS(sum_range,[range1, criteria1], [range2, criteria2],…) | |
| SUMPRODUCT | SOMMEPROD | SUMPRODUCT(array1,array2,array3, …) | Unlike SUM, does not take strings into account. Calculations of the type SUMPRODUCT(Range1 operator Range2) are not allowed (example SUMPRODUCT(D1:D2+E1:E2/2) |
| SUMSQ | SOMME.CARRES | SUMSQ(number1,number2,…) | Excel also counts booleans or text entered directly as arguments |
| SUMX2MY2 | SOMME.X2MY2 | SUMX2MY2(array_x,array_y) = sum (x^2 – y^2) | |
| SUMX2PY2 | SOMME.X2PY2 | SUMX2PY2(array_x,array_y) = sum (x^2 + y^2) | |
| SUMXMY2 | SOMME.XMY2 | SUMXMY2(array_x,array_y) = sum (x – y)^2 | |
| TAN | TAN | TAN(number) | |
| TANH | TANH | TANH(number) | |
| TRUNC | TRONQUE | TRUNC(number, num_digits) |
Statistics
| Name (EN) | Name (FR) | Syntax | Remarks |
| AVEDEV | ECART.MOYEN | AVEDEV(number1,number2,…) | |
| AVERAGE | MOYENNE | AVERAGE(number1,number2,…) | Excel also counts booleans or text entered directly as arguments |
| AVERAGEA | AVERAGEA | AVERAGEA(number1,number2,…) | |
| AVERAGEIf | MOYENNE.SI | AVERAGEIF(range,criteria,[av_range]) | From version 3.9range must have a number of elements <= to av_range otherwise => #N/A! (if not, Excel completes range) |
| AVERAGEIFS | MOYENE.SI.ENS | AVERAGEIFS(av_range,rng1,crit1,rng2,crit2) | From version 3.9 |
| COUNT | NB | COUNT(value1,value2,…) | |
| COUNTA | NBVAL | COUNTA(value1,value2,…) | |
| COUNTBLANK | NB.VIDE | COUNTBLANK(range) | |
| COUNTIF | NB.SI | COUNTIF(range,criteria) | |
| COUNTIFS | NB.SI.ENS | COUNTIFS(range1, criteria1,range2, criteria2…) | Function of Excel 2007 and above |
| COVAR | COVARIANCE | COVAR(array1,array2) | |
| DEVSQ | SOMME.CARRES.ECARTS | DEVSQ(number1,number2,…) | |
| MAX | MAX | MAX(number1,number2,…) | |
| MAXA | MAXA | MAXA(number1,number2,…) | |
| MEDIAN | MEDIANE | MEDIAN(number1,number2,…) | |
| MIN | MIN | MIN(number1,number2,…) | |
| MINA | MINA | MINA(number1,number2,…) | |
| STDEV | ECARTYPE | STDEV(number1,number2,…) | |
| STDEVP | ECARTYPEP | STDEVP(number1,number2,…) | |
| VAR | VAR | VAR(number1,number2,…) | |
| VARP | VAR.P | VARP(number1,number2,…) |
Text
| Name (EN) | Name (FR) | Syntax | Remarks |
| CHAR | CAR | CHAR(number) | |
| CLEAN | EPURAGE | CLEAN(text) | |
| CODE | CODE | CODE(text) | |
| CONCATENATE | CONCATENER | CONCATENATE (text1,text2,…) | |
| EXACT | EXACT | EXACT(text1,text2) | |
| FIND | TROUVE | FIND(find_text,within_text,start_num) | |
| FIXED | CTXT | FIXED(number[,decimals,no_commas]) | |
| LEFT | GAUCHE | LEFT(text,num_chars) | |
| LEN | NBCAR | LEN(text) | |
| LOWER | MINUSCULE | LOWER(text) | |
| MID | STXT | MID(text,start_num,num_chars) | |
| PROPER | NOMPROPRE | PROPER(text) | |
| REPLACE | REMPLACER | REPLACE(old_text,start_num,num_chars,new_text) | |
| REPT | REPT | REPT(text,number_times) | |
| RIGHT | DROITE | RIGHT(text,num_chars) | |
| SEARCH | CHERCHE | SEARCH(find_text,within_text,start_num) | |
| SUBSTITUTE | SUBSTITUTE | SUBSTITUTE(text,old_text,new_text,instance_num) | |
| T | T | T(value) | |
| TEXT | TEXTE | TEXT(value, format_text) | |
| TRIM | SUPPRESPACE | TRIM(text) | |
| UPPER | MAJUSCULE | UPPER(text) | |
| VALUE | CNUM | VALUE(text) |
Finance
| Name (EN) | Name (FR) | Syntax | Remarks |
| NPV | VAN | NPV(rate, value1, value2,…) | |
| XNPV | VAN.PAIEMENTS | XNPV(rate, values, date) |
Named fields
When importing an Excel file into Design, the named fields are imported.
The following named fields are maintained (local or global)
- reference (absolute)
- value
- formula without relative reference (except matrix formulas).
A name field can be used in graphs. The engine correctly handles the reference operator on the fields. In the table below, the field named “Quantity” is the data range C6:C8, the field named “CA” = D6:D8. In E6, the formula is “Quantity*CA”, which in this case is C6*D6.
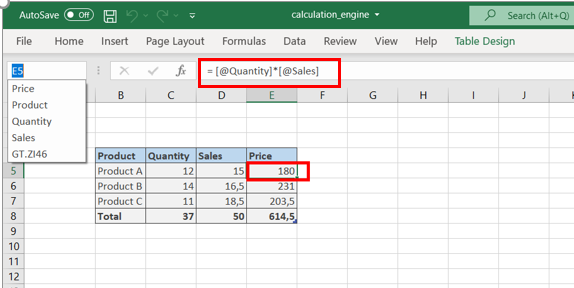
The following fields are not imported:
- hidden field
- #REF!
- invalid formula (for GT)
All global named fields are reimported at each Excel import, even those that are not in the import field. The list of named fields can be viewed (but not modified) via “Tools” –> “View Names”. Duplicates with the names generated in the Excel export are checked when saved in Design (only a warning). However, a collision is allowed if the name field and the component coincide.
Table function in Excel 2007 (and higher)
The Table function in Excel is not supported.


